The 4 Best AM5 Motherboard for 7800X3D/7950X3D – If you are looking for a motherboard for your AMD 7800x3d or 7950x3dthen you are in the right place, in this article, I will show you some AM5 socket motherboards that you can use right now, so read this post completely to get a details information.
Talking about the AM5, this is a new processor socket from AMD that is a little different from the old AM4 sockets as it offers the latest DDR5 RAM with more cache size, better power consumption, and more pins, and the results are super smooth gameplay.
If you compare with AM4 with the newest AM5 then the performance is definitely high on the newest one Also you can use more graphics on the new one as it has more slots. The AM5 was launched last year and the AM4 was launched in 2016 so there isso many changes in the new in technology-wise.
If you are using the AMD 7800x3d and want to use the newest motherboard with AM5 then below I shared some of the best motherboards that you can choose.
Best AM5 Motherboard for 7800x3d or 7950x3d
These are the some of great options that you can pick, Before choosing an AM5 motherboard you should think about the budget as it costs high compared to the old AM4 motherboard.
1. ASUS TUF Gaming B650-PLUS

This is the ASUS TUF Gaming B650-PLUS which offers an AM5 socket with DDR5, Wi-Fi 6 for better connectivity, and more space for graphics cards so you can keep more graphics cards compared to an AM4 model. Asus is one of the best motherboard-producing companies that give you reliable performance with better power consumption that runs for a long time, it will be the best choice for you. The best thing about this motherboard is the price tag is reasonable.
2. GIGABYTE X670 AORUS Elite AX
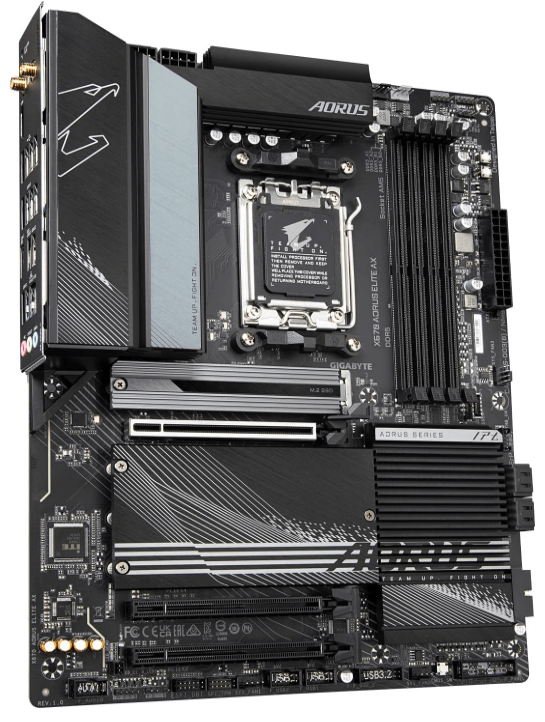
This is the high-end AM5 support motherboard from Gigabyte one of the most popular in the market as it offers an extreme gaming experience with top-notch graphics quality, It is compatible with the Ryzen 700 series processors with DDR5 RAM, 64GB memory, and advanced cooling system so play heavy games for long without any heating issues from Motherboard. The [price definitely justifies the specs and you should check this out.
3. ASUS ROG Strix B650-A
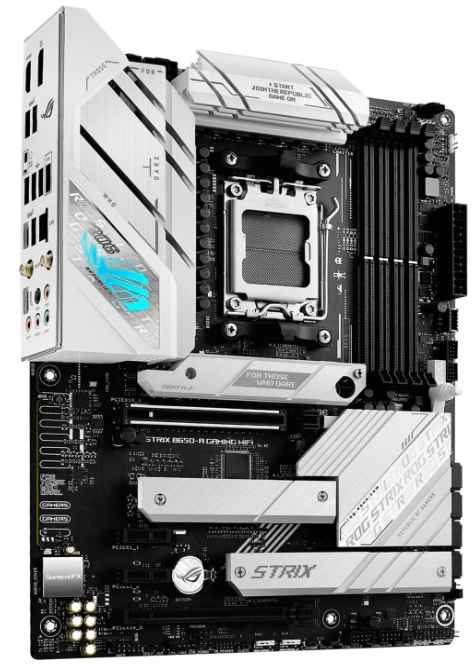
I know it’s a B650 chipset but the other specs are so nice, as it has Type C, PSIe 4.0, Wifi 6E, 128GB memory, and of course AM5 support with amazing performance, with many ports so you can customize it with accessories and stuff. The price is huge so choose if you think it is perfect for your setup.
4. MSI PRO B650M-P ProSeries
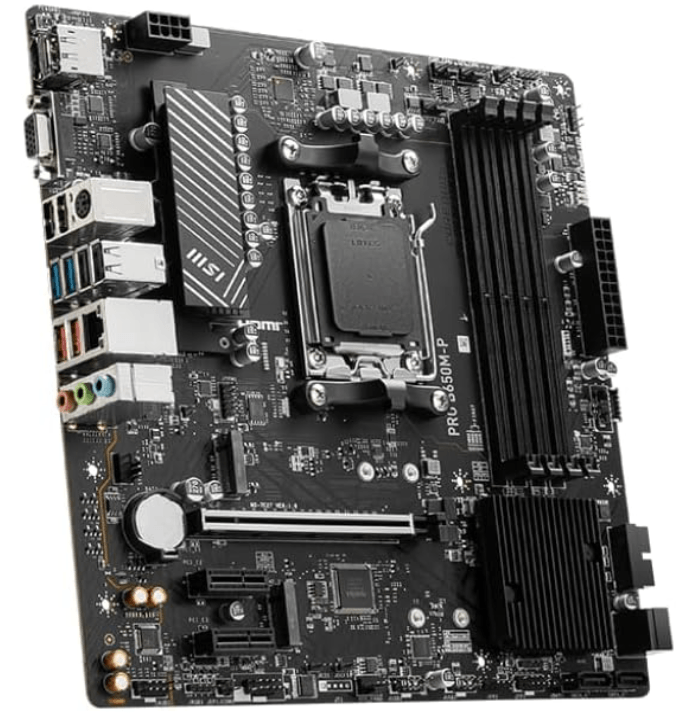
If your budget is totally but want an AM5 socket motherboard then you can choose this as it has a very low price tag compared to other motherboards like the X670 chipset It is a super balanced motherboard with all the features that you expect from a below $200 motherboard with Ryzen 7000 series supports then this is the right for you.
The difference between X670 and B650 chipsets
PCIe Lanes: X670 motherboards typically have more PCIe lanes available compared to B650 motherboards. This means you can have more high-speed PCIe devices (like NVMe SSDs and GPUs) connected simultaneously without bandwidth limitations.
USB Ports: X670 motherboards usually offer more USB ports, including USB 3.2 Gen 2 and Gen 1 ports. B650 motherboards have fewer USB ports but still offer good connectivity.
Overclocking Support: Both B650 and X670 motherboards support overclocking for compatible AMD Ryzen processors. However, X670 motherboards may offer slightly better power delivery and cooling solutions for extreme overclocking.
Price: X670 motherboards tend to be more expensive than B650 motherboards due to the additional features and PCIe lanes they offer.
Chipset Fan: X670 motherboards often have a chipset fan to cool the chipset itself, which can be a point of concern for some users in terms of noise and potential reliability. B650 motherboards typically do not have a chipset fan.
Read: The Ultimate Gaming Monitor for PS5
How to choose the right motherboard
Choosing the right motherboard is crucial for building a stable and efficient PC. The motherboard serves as the foundation for your system, connecting all your components together. To select the right motherboard, consider the following factors:
- CPU Compatibility: Ensure that the motherboard is compatible with your chosen CPU. Motherboards are designed for specific CPU sockets, such as LGA 1200 for Intel or AM4 for AMD. Check the motherboard’s CPU support list to confirm compatibility with your processor model.
- Chipset: The chipset determines the motherboard’s features and capabilities. Different chipsets offer varying levels of performance, connectivity, and overclocking support. Choose a chipset that matches your needs and budget.
- Form Factor: Motherboards come in various form factors, including ATX, Micro ATX (mATX), and Mini-ITX. The form factor affects the size of your PC case and the number of expansion slots and ports available. Ensure the motherboard fits comfortably in your case and provides the necessary connectivity.
- Expansion Slots: Consider the number and type of expansion slots you require. PCIe x16 slots are essential for graphics cards, while PCIe x1 slots can accommodate additional cards like Wi-Fi adapters, sound cards, or NVMe SSDs. If you plan to run multiple GPUs, ensure the motherboard supports SLI or CrossFire.
- Memory Support: Check the motherboard’s memory compatibility and capacity. Determine the maximum RAM capacity and supported memory speeds. Ensure it supports the RAM type (e.g., DDR4 or DDR5) that you plan to use.
- Storage Options: Consider your storage needs. Look for SATA ports for traditional hard drives and SSDs, M.2 slots for NVMe SSDs, and support for RAID configurations if necessary.
- Connectivity: Evaluate the motherboard’s I/O options, including USB ports, audio jacks, Ethernet, and Wi-Fi. Choose a motherboard that meets your connectivity requirements. Built-in Wi-Fi and Bluetooth can be convenient features.
- Overclocking: If you intend to overclock your CPU or GPU, select a motherboard that supports overclocking features. Look for a chipset with good VRM (Voltage Regulator Module) design and cooling solutions.
- Build Quality: Consider the build quality and durability of the motherboard. High-quality components, reinforced PCIe slots, and good thermal solutions can enhance long-term reliability.
- Brand and Reviews: Research motherboard manufacturers and read reviews from reputable sources. Well-established brands often provide better customer support and reliability.
- Price: Set a budget for your motherboard and find options that offer the features you need within that budget. Keep in mind that more expensive motherboards typically come with additional features and better build quality.
- Future Compatibility: Consider future upgrades. Ensure the motherboard has room for expansion and supports upcoming technologies.
- BIOS and Software: Check the motherboard’s BIOS interface and available software tools. A user-friendly BIOS and useful software can make system management easier.
- Aesthetics: While not as critical as other factors, motherboard aesthetics can be important if you care about the overall look of your PC. Some motherboards offer RGB lighting and customizable designs.
Remember that the right motherboard depends on your specific requirements, so prioritize the features that matter most to you. Compatibility with your CPU and other components is paramount, so double-check compatibility lists and user reviews to ensure a smooth build process.
- LG 45GR65DC-B Review – 200Hz, 1500R, DisplayHDR 600
- Sceptre C345B-QUT168 Review – 165Hz, 1500R, Tilt-Only
- LG 32GQ750-B Review – 4K, 144Hz, Weak Color Accuracy
- Asus VG34VQL3A Review – 180Hz, HDR 400, 123% sRGB
- LG 27GR93U-B Review – 4K, 144Hz, DisplayHDR 400
How to keep your motherboard healthy for a long time
Maintaining your motherboard is essential to ensure the long-term stability and reliability of your computer. Here are some tips for maintaining your motherboard:
Regular Cleaning:
Power off and unplug your computer before cleaning. Use compressed air to remove dust and debris from the motherboard, especially around the CPU socket, RAM slots, and PCIe slots. Gently clean the motherboard’s surface with a soft, anti-static brush or a lint-free cloth.
Cable Management:
Keep cables organized and secured to prevent them from interfering with fans, heatsinks, or other components on the motherboard. Ensure that cables are not pinched or bent excessively, which could cause damage or interference.
CPU and Cooler Maintenance:
If you use an air cooler for your CPU, clean it periodically to remove dust buildup. Dust can affect cooling performance. If you’re using a liquid cooler, check for leaks and ensure that the pump is functioning correctly.
BIOS and Driver Updates:
Periodically check for BIOS updates on the motherboard manufacturer’s website. Updates can improve system stability, compatibility, and performance. Keep your motherboard drivers up to date, especially graphics cards, chipsets, and network drivers.
Monitor Temperatures:
Use monitoring software to keep an eye on your CPU and motherboard temperatures. High temperatures can indicate cooling issues. Ensure that your CPU cooler is seated correctly and that thermal paste is applied properly.
Static Electricity Precautions:
When handling your motherboard, ground yourself to prevent static electricity discharge, which can damage sensitive components. Use an anti-static wrist strap or touch a grounded metal object before touching the motherboard.
Read: How to Browse Reddit App Anonymously – Stay Private
Keep Dust Out:
Maintain a clean and dust-free computer case by using dust filters on intake fans. Ensure that the computer case is placed in a clean environment to minimize dust intake.
Power Surge Protection:
Use a surge protector or uninterruptible power supply (UPS) to protect your computer from power surges and outages. These can damage the motherboard.
Read: The 5 Best Monitors for Photo Editing
Inspection:
Periodically inspect the motherboard for physical damage, such as bent pins, loose components, or damaged connectors. Address any issues promptly.
Backup BIOS Settings:
Some motherboards allow you to save and restore BIOS settings. Create a backup of your BIOS settings in case you need to reset them or if there’s a BIOS update failure.
Avoid Overclocking:
Overclocking can put additional stress on the motherboard and other components. If you overclock, do so responsibly and ensure proper cooling.
RAM and Component Installation:
When adding or removing RAM and other components, handle them with care to avoid bending pins or damaging slots.
Storage Maintenance:
Periodically check and optimize your storage drives for performance and health using built-in tools or third-party software.
How motherboard Works
A motherboard, also known as the mainboard or system board, is a crucial component of a computer that serves as a central hub connecting and coordinating various hardware components. It provides the physical and electrical connections necessary for these components to communicate and work together harmoniously. Here’s an overview of how a motherboard works:
- Physical Structure: A motherboard is a large, flat circuit board made from non-conductive materials like fiberglass. It features various components, connectors, and traces (conductive pathways) that interconnect everything.
- CPU Socket: The central processing unit (CPU) socket is one of the most critical components on the motherboard. The CPU is the “brain” of the computer, responsible for executing instructions and performing calculations. It plugs into the CPU socket, and the motherboard provides power and data connections to the CPU.
- Chipset: The motherboard contains one or more chips known as chipsets. These chipsets act as controllers and help manage communication between different hardware components. The Northbridge and Southbridge are two common chipset components, but modern motherboards often integrate their functions into a single chip.
- Northbridge: Traditionally, it handled tasks like memory and graphics card communication but has become less relevant with integrated graphics and modern CPU architectures.
- Southbridge: Manages lower-speed peripherals like USB ports, SATA drives, and audio components.
- Memory Slots: Motherboards have slots for installing system memory modules (RAM). RAM is essential for temporarily storing data and instructions that the CPU needs to access quickly. The motherboard’s memory controller, often part of the CPU or integrated into the Northbridge, manages data transfer between the RAM and the CPU.
- Expansion Slots: These slots allow you to install additional hardware components like graphics cards, sound cards, network cards, and more. Common expansion slot types include PCIe (Peripheral Component Interconnect Express) and older PCI (Peripheral Component Interconnect) slots.
- Peripheral Connectors: Motherboards include connectors for various peripherals and devices, including USB ports, audio jacks, SATA ports for connecting hard drives and SSDs, Ethernet ports, and more. These connectors are managed by the Southbridge and often controlled by dedicated controllers or chips on the motherboard.
- Power Connectors: The motherboard has connectors for receiving power from the computer’s power supply unit (PSU). The primary power connector is the ATX connector, and there may be additional connectors for providing power to the CPU, graphics card, and other components.
- BIOS/UEFI: The Basic Input/Output System (BIOS) or Unified Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI) is firmware stored on a chip on the motherboard. It initializes hardware components during the boot process, performs system checks, and loads the operating system from storage devices like hard drives or SSDs.
- Data Bus: The motherboard features a complex network of traces that act as a data bus, connecting the CPU, memory, storage devices, and other components. These traces carry data and signals between the components at high speeds.
- Voltage Regulation: The motherboard includes voltage regulator modules (VRMs) responsible for converting the high-voltage power from the PSU into the lower voltages required by the CPU and other components. This ensures stable and reliable power delivery.
In summary, a motherboard serves as the backbone of a computer, providing the infrastructure for various hardware components to interact with each other. It manages power distribution, data transfer, and communication among these components to enable the computer to function as a cohesive unit.
Conclusion
Selecting the right motherboard is vital for a smooth PC build. Prioritize compatibility with your CPU, desired features, and form factor. Your chosen motherboard will influence your system’s performance and future upgradability, so choose wisely to meet your specific needs and budget. I hope this piece of information helps you to choose the best motherboard and also how to maintenance and the different chipset comparisons. Bookmark our site to get all types of tech content on your fingertip.
Tech-Enthusiast and Founder/Author of Techotn.com and also a passionate Pinterest Marketer at Sajalmanjhi.com. Follow me on X twitter.com/ManjhiSajal